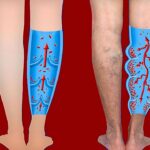
Health is the main priority of every individual, be it physical, mental, emotional, or vascular. Hypertension is a very common body complication that often occurs when the human vascular system is not functioning properly. It can be because of weakened blood circulation, arterial loss, impaired blood vessels, weak pulse, higher blood pressure, cardiovascular risks, and vascular pains. The vascular system needs to be energized again by improving the structural and functional ability of the blood vessels.
The most common way to do so is to inject medicinal drugs that are assumed to directly act upon blood arteries, veins, capillaries, lymphatic vessels, etc. They dilate the opening of vessels, preventing the tightening of muscles and narrowing veins.
Medications for improved vascular health
The problems of the human vascular system are commonly observed in the human population, with a high frequency of prevalence found in females. Anti-hypertensive agents and vasodilators are considered quite efficient as the medicinal cure for increasing vascularity of vessels. Some of the common examples are
- Calcium channel blockers
- Benazepril
- Cilostazol
- Aspirin
- Lisinopril
- Losartan
- Hydralazine
- Minoxidil
- Nitrostat
- Pentoxifylline
- Cardizem
However, the dose management of these therapeutic drugs is also necessary to test the clinical concentration of the medicine apt for intake. Monitoring medication for better vascular health is the direct way to measure oxygen concentration, heartbeat, heart pumping rate, and blood pressure, which are the main targets of these medicines, referring to the efficacy of the drug intake.
Thus, it offers the best possible numerical and visual condition of improved vascular health when medicinal scheduling is ongoing with the patient. Arterial hypertension being treated by medicines need to be monitored at regular intervals. This help to define the curing stage of vascular diseases like
- Angina
- Congestive heart failure
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Postpartum preeclampsia
Arterial monitoring on medicinal drugs in vascular treatments
Numerous heterogeneous recommendations are listed to monitor vascular treatments. The easiest and most convenient way to achieve it is by measuring blood pressure using a barometer on the left arm for seven consecutive days. If the BP values are about nominal, then it can be predicted that the body is reacting positively to the vascular medicines.
A pulse oximeter is another instrumental device used to measure the oxygen concentration in the blood after the medicine is ingested as a remedy for vascular abnormalities. These strategies help to asses and monitor medication for better vascular health. In this way, the doctor can prescribe that the medicine used continuously effectively controls vascular complexities and whether the patient needs to adhere to these for a long time. The pill count may also get varied after the clinical testing and monitoring of the drug’s therapeutic action.
This clinical approach is critical for patients with extreme vascular conditions as they must not be linked to poor medicinal routine, worsening their health. For such purposes, home, office, and other timely blood pressure measurements of the patient is an evidentiary proof for doctors to test the medicinal effect. Therapeutic inertia must be maintained to make medicinal monitoring safe and secure for patient deliverance.