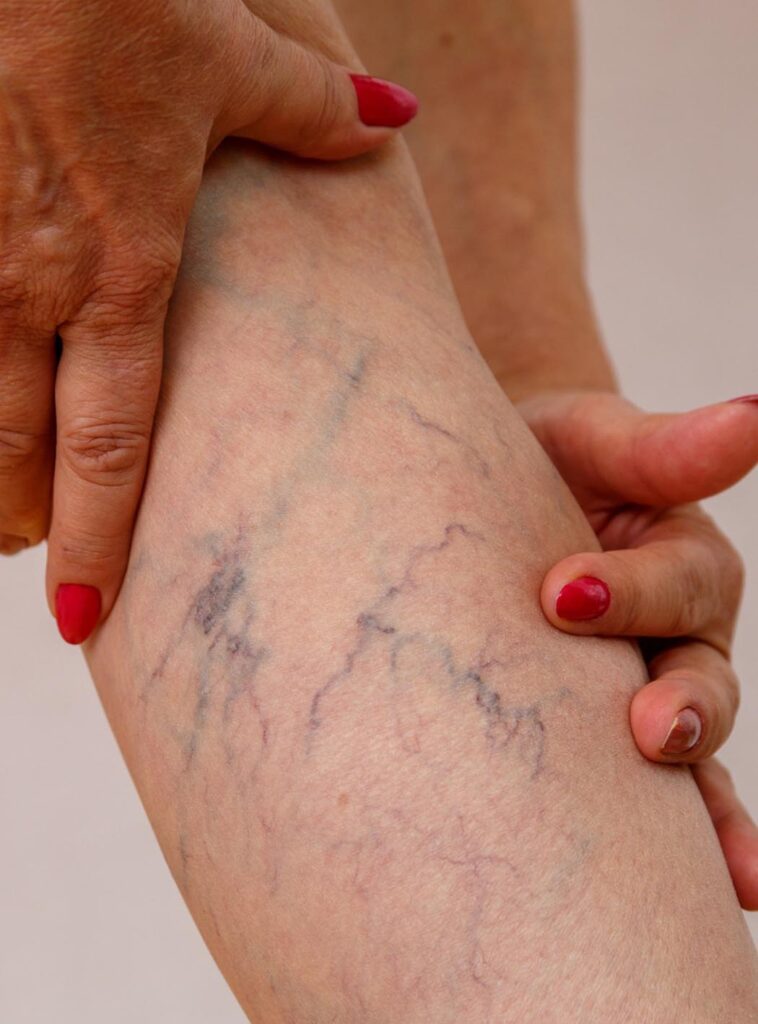
The clinical diagnosis of varicose veins is initially done via physical examination. The areas of concern in the physical analysis are the type, location, depth, extent, and cause of the varicose veins. One of the first identification is assumed by deep pulse examination. The symptoms are tested for any mild, acute, or chronic venous diseases or varicose veins like vascular ulceration and atrophie blanch.
Two major medical tests which are denoted as the Brodie-Trendelenberg test and the Perthes test are employed for detecting the severity of venous illnesses. These clinical investigations primarily distinguish between superficial venous, deep venous deficiency, and venous obstruction. Venus ultrasonography is a modernized medical approach that is perfect for detecting deep superficial thrombosis. Any iliac vena cava compression that is suspected can be well-imaged by invasive venography, tomographic and magnetic resonance.
In the world population, the epidemiological data for varicose veins is reported in such a way that there is a minor stigma of varicose veins state in adults.
About 50-55% of females and 40-45% of males are expected to experience venous diseases, with half and even less the rate of varicose veins. Nearly, 20-25% of females and 10-15% of males are found to be suffering from visible varicose veins with multiple genotypic and phenotypic factors.