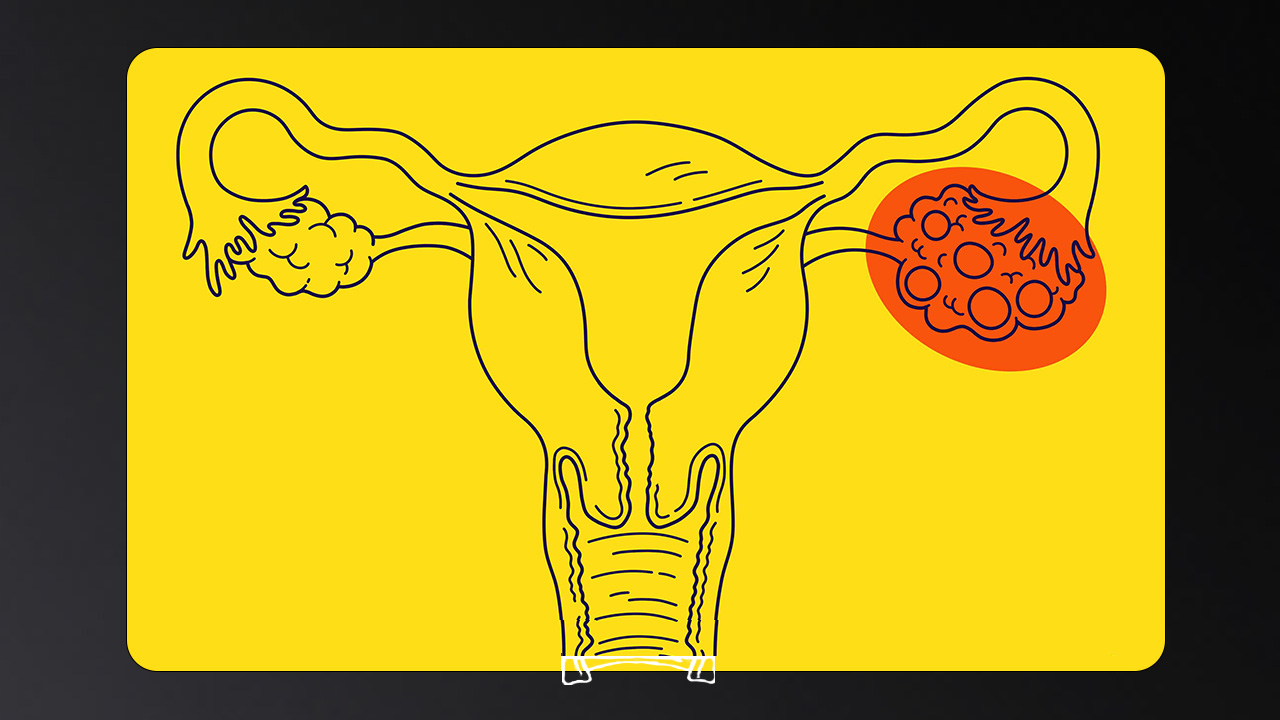
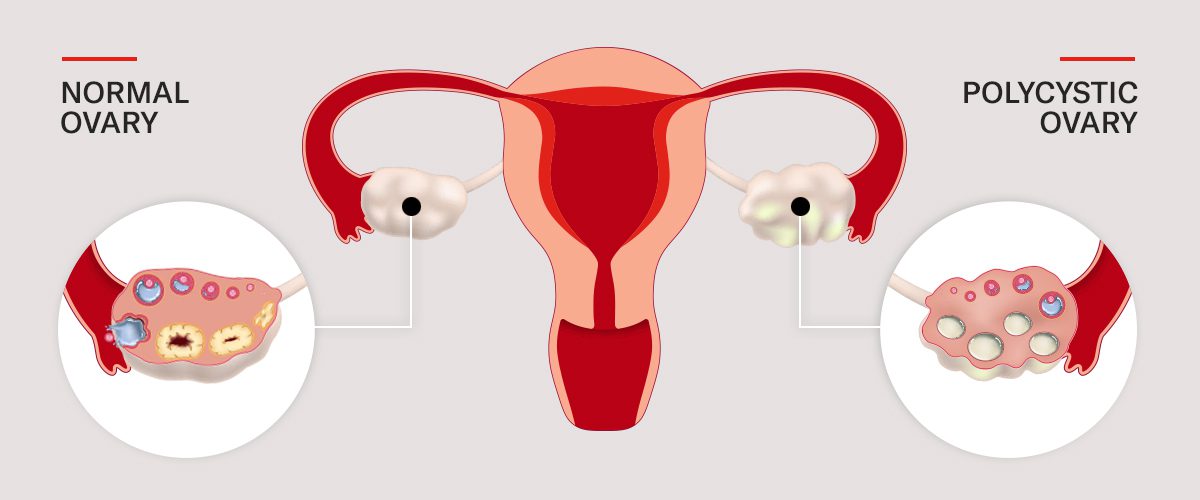
PCOS, or polycystic ovary syndrome, is a hormonal disorder characterized by elevated levels of androgens (male hormones). PCOS can lead to multiple ovarian cysts, irregular periods, and fertility issues. It is closely associated with metabolic problems, specifically insulin resistance, that may result in the development of type II diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular disorders.
Critical symptoms of PCOS:
- Irregular or absent menstrual periods
- Weight gain or difficulty losing weight
- Excessive hair growth (hirsutism) on the face, chest, or back
- Acne or oily skin
- Thinning hair or hair loss
- Infertility (in some cases)
- Multiple small cysts on the ovaries
What are Uterine Fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are benign growths within the uterus from its muscle tissue. They are non-cancerous and are also known as myomas or leiomyomas. They vary in size, shape, and location. Critical symptoms of fibroids:
- Heavy and irregular menstrual bleeding
- Painful menstruation
- Back pain
- Bloating or abdominal swelling
- Fatigue
- Constipation
- Frequent urination
Common Link between PCOS and Fibroids
PCOS and fibroids are two different conditions but share a common link, which is hormonal imbalance. In both situations, reproductive hormones (estrogen and progesterone) are crucial alongside other accompanying conditions.
Estrogen Dominance: Estrogen dominance is typical in both conditions. It leads to irregular ovulation, while in fibroids, it can promote fibroids’ growth. The dynamics may be different, but estrogen plays a critical role.
Role of Progesterone: In PCOS, progesterone levels are reduced due to irregular ovulation, resulting in overgrowth in the uterine lining. This phenomenon could lead to the development of fibroids, though the mechanism is not fully supported.
Insulin Resistance: Both fibroids and PCOS are more common in women with insulin resistance. Insulin resistance is a condition where the body’s cells do not respond effectively to insulin, leading to high levels of blood sugar. In PCOS, insulin resistance can result in elevated androgen production. This hormonal imbalance can further disrupt the average production of estrogen and progesterone, contributing to fibroids.
Can PCOS lead to fibroids?
While there is no definitive proof that PCOS can directly lead to fibroid development, both conditions can coexist due to shared risk factors. The hormonal environment created by PCOS can increase the likelihood of fibroid growth due to the overgrowth of the uterine lining.
Management of both conditions
For women who may have fibroids and PCOS together, appropriate protocols are necessary for the management, such as:
- Hormonal treatments
- Weight management
- Lifestyle changes
- Insulin sensitizers
PCOS and fibroids are two distinctive conditions, each with its own set of challenges. However, they share various standard links associated with hormonal imbalance. While it may not directly lead to fibroid development, it may increase the likelihood. Therefore, a comprehensive approach is required to manage both conditions effectively and improve the quality of life.