Sometimes, women’s reproductive health can be a bit of a puzzle, with overlapping symptoms that don’t always tell you what is going on. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and uterine fibroids (or fibroid tumors) are both prime examples of two common conditions.
However, both conditions can significantly impact health and fertility, but two different things cause them and demand two other treatments. In this article, let’s take a closer look at the five significant differences between PCOS and fibroids so you can better understand these conditions.
What Triggers Each Condition?
PCOS is primarily a hormonal imbalance. The main culprits are elevated androgen levels (male hormones), insulin resistance, and genetic predisposition. PCOS disrupts ovulation, often leading to the formation of tiny cysts on the ovaries.
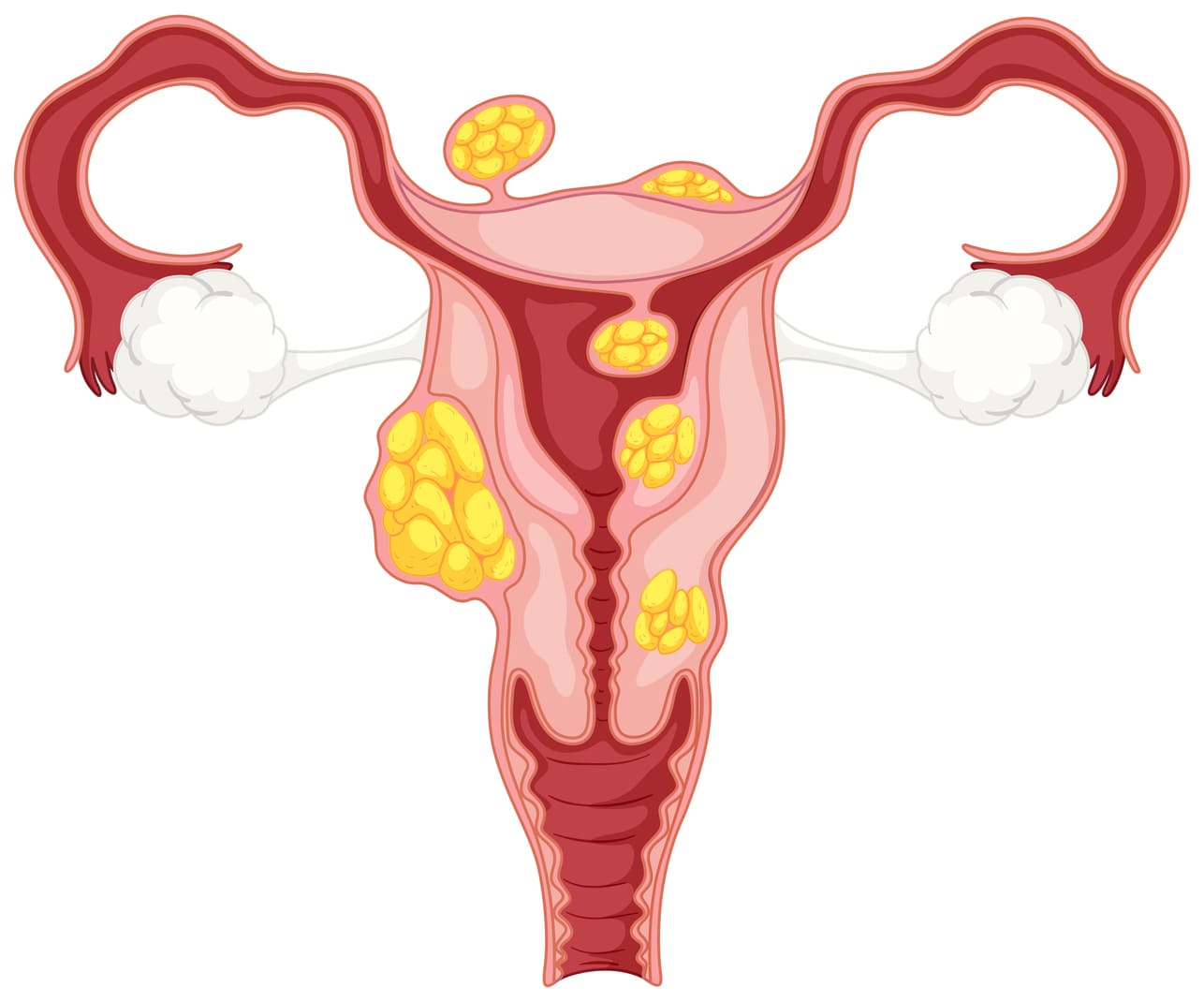
On the other hand, uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths that form in or on the muscular wall of the uterus. They are linked to hormonal fluctuations, particularly estrogen and progesterone, and genetic factors. Unlike PCOS, fibroids are not directly tied to insulin resistance or androgen levels.
Location in the Body: Ovaries vs. Uterus
The primary location of these conditions also sets them apart.PCOS primarily affects the ovaries. The hormonal imbalances caused by PCOS interfere with regular ovulation, which can throw menstrual cycles off balance.
Fibroids grow in or on the uterine wall. Depending on their size and location, they may cause symptoms like pelvic pressure, discomfort, or even fertility challenges. Unlike PCOS, fibroids are entirely unrelated to ovarian function.
How Do They Present Themselves?
PCOS is a hormonal disorder that affects women and is characterized by a range of symptoms. These can include irregular or absent menstrual periods, excessive hair growth (hirsutism), acne and oily skin, and weight gain or obesity. PCOS is also associated with insulin resistance, which can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths that develop within the muscular wall of the uterus. Common symptoms associated with fibroids include heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain or pressure, frequent urination, and pain during intercourse. In some cases, individuals may also experience lower back pain.
Light and Irregular vs. Heavy and Prolonged
Women with PCOS often experience irregular or missed periods due to disrupted ovulation. Hormonal imbalances mean the menstrual cycle doesn’t follow a consistent pattern.
Fibroids are more likely to cause heavy and prolonged periods. This is because they can directly affect the uterine lining, leading to excessive bleeding.
Impact on Fertility
Irregular ovulation is the main issue. Without consistent ovulation, it’s harder for women to conceive naturally. However, with proper treatment and lifestyle changes, many women with PCOS successfully conceive.
Fibroids may interfere with fertility by distorting the shape of the uterus or blocking the fallopian tubes. Large fibroids can also hinder embryo implantation. The impact often depends on the size, location, and number of fibroids.
Hormonal Imbalances
Elevated androgen levels and insulin resistance mark this imbalance. Symptoms like acne, hair growth, and irregular cycles stem from this imbalance.
Fibroids grow in response to estrogen and progesterone. They may enlarge during pregnancy and shrink after menopause when hormone levels decline.
Diagnostic Tools
Diagnosed using a combination of clinical assessments, hormonal tests, and ultrasound imaging. The ultrasound often reveals multiple small cysts on the ovaries.
Typically detected through pelvic exams, ultrasounds, or, in some cases, MRI scans to determine their size and location.
Treatment Options
Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing long-term complications. This includes lifestyle changes, medications to regulate hormones, and sometimes fertility treatments.
Treatment depends on severity and symptoms. Options range from medications to control bleeding, minimally invasive procedures, or surgical removal for larger fibroids.
Why Understanding the Differences Matters
There is often a difference between PCOS and fibroids, even though they can coexist and share some symptoms. The difference is essential because PCOS and fibroids are correctly diagnosed and treated.
Take the instance of PCOS-induced irregular periods or heavy bleeding from fibroids; they demand a different approach. You get proper care for your condition when you know the root cause.