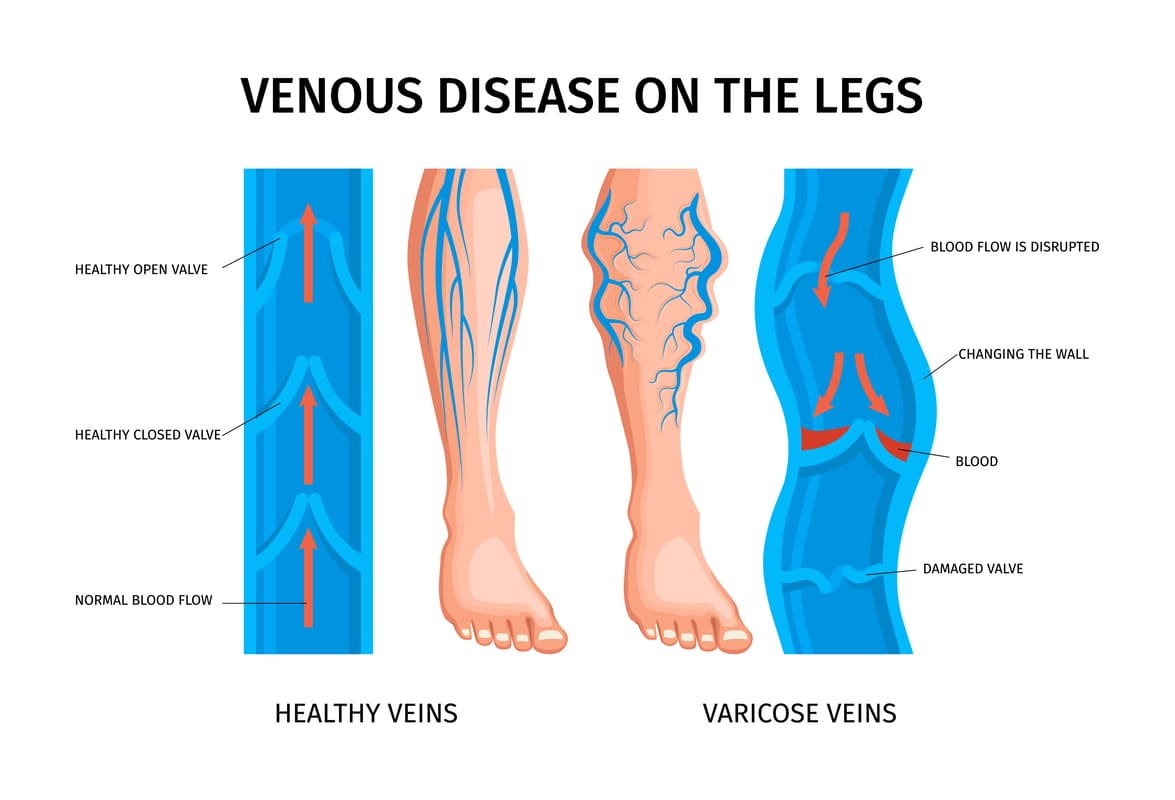
Varicose veins, those twisted, enlarged veins often visible on the legs, are a common condition affecting up to 70% of the global population. While both men and women can develop varicose veins and other forms of venous disease, there are some key differences in how these conditions present and are managed between the sexes.
Are Women More Prone to Varicose Veins?
According to statistics, varicose veins are twice as common in women as in men. Several factors contribute to this discrepancy, and hormones are one in particular.
Estrogen and progesterone hormones, which fluctuate over a woman’s life, are thought to weaken vein walls and upset normal blood circulation. Blood pooling in the veins results from this disruption, which can cause the veins to swell or become varicose.
Pregnancy further exacerbates this issue by affecting blood flow in the veins and pelvis, increasing pressure within the leg veins. This explains why many women experience the onset or worsening of varicose veins during pregnancy.
Do Men Experience More Severe Issues?
While women are more likely to develop varicose veins, observations suggest that men are more prone to neglecting the issue until it reaches a more severe stage. While severe complications can occur in both sexes, men often delay seeking medical attention.
Interestingly, some studies have shown that up to 75% of hospital admissions for varicose veins are men. This occurs for many reasons, and many contributing factors have been suggested—measures such as smoking, heavy lifting, standing for prolonged periods, and drinking alcohol.
However, most people threw out the factors as definitive scientific verification was lacking. The effects of venous diseases do not vary significantly between men and women. The difference is the time required for treatment.
Understanding the Underlying Factors
The development of varicose veins is a complex process, depending on many factors. Genetics (a family history does increase risk), embryologic persistence (congenital vein abnormalities), age (loss of vein elasticity and weakened valves), hormones (particularly fluctuations in women), and other contributing factors such as lifestyle, occupation, and overall health.
Treatment and Management
Though gender-based differences in prevalence and contributing factors exist, the core treatment and management strategies for varicose veins are similar. What they do is focus on promoting healthy circulation and lessening vein strain.
Key recommendations include adopting a healthy lifestyle by quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake, engaging in regular physical activity to enhance blood flow, and consuming a nutritious diet rich in fibre, vitamins, and antioxidants like leafy greens, berries, and apples while reducing trans and saturated fats and processed foods.
The Importance of Early Intervention
Early professional advice from a vein specialist is essential regardless of gender, as it’s the best way to manage varicose veins. Early intervention can prevent the condition from progressing and avoid potentially serious complications.
Proactively tackling any medical concern, no matter how minor, is always better than waiting until it worsens. This is particularly relevant for men, who may be more likely to put off seeking treatment.