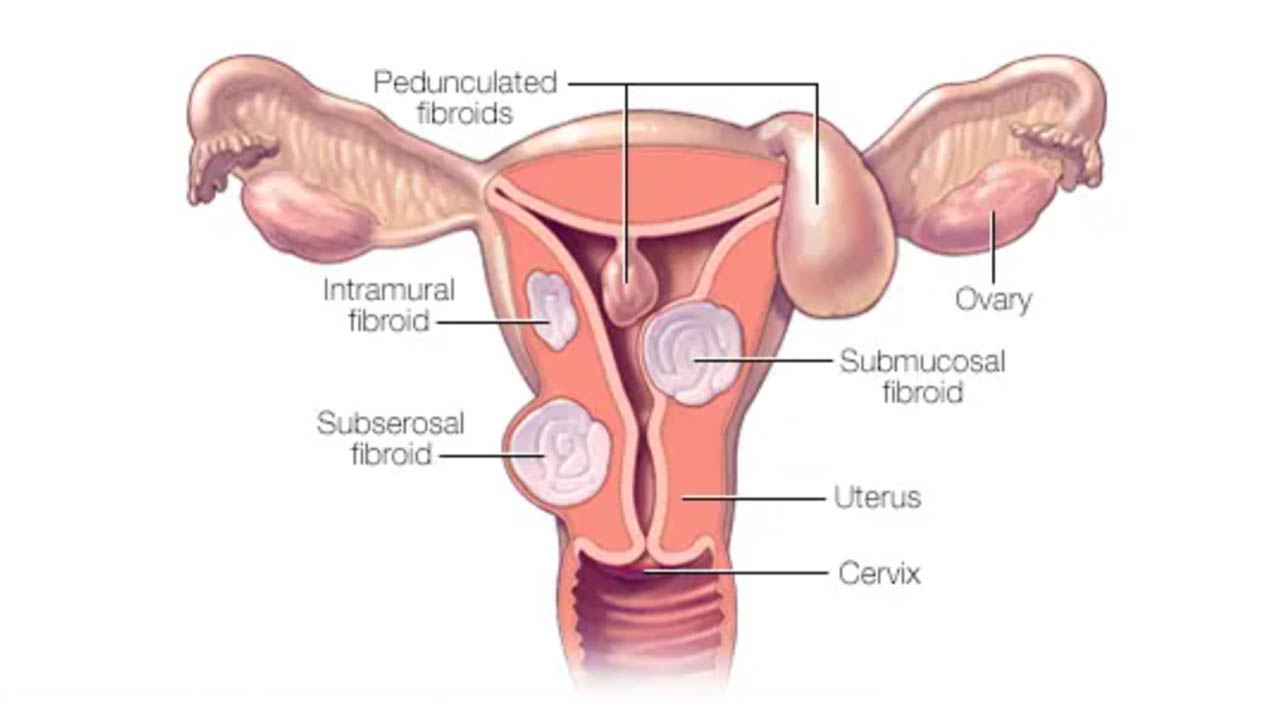
Fibroids and cysts, both, are very common among females. Uterine fibroids are the muscular growths of several centimeters that are often left undetected because they are not cause any signs or symptoms. 50% of all women are known to have developed fibroids by the age of 50. Only about 25% of the women with fibroids experience symptoms.
What are ovarian cysts?
Ovaries are generally responsible for producing hormones and to regulate the reproductive symptoms. Ovarian cysts can be benign and malignant, the benign cysts are the dermoid and endometriotic chocolate cysts. The malignant cysts include germ cells, ovarian cancers, etc. The ones forming in the muscular walls of the uterus and known as fibroids.
However, the ones developing in or on the ovaries are referred to as cysts. Fibroids are non-cancerous tumors, while cysts are fluid-filled pouches. Even though they develop in different places, they have similar symptoms and these symptoms can make you wonder what is wrong.
Fibroids have a direct impact on the uterus while cysts have a direct impact on the ovaries, their treatment greatly depends on the symptoms or the family plans.
Difference Between Fibroids and Cysts
Location: Uterine fibroids are known to develop in or on the uterus from the muscle layer, while cysts develop on the ovaries.
Appearance: Uterine fibroids are a dense, firm non-cancerous tumor however the ovarian cysts appear to be like fluid-filled sacs.
High risk at age: Uterine fibroids have a high risk of developing among females before menopause and ovarian cysts are especially common before menopause.
Symptoms of Fibroids
⦁ Pelvic pain
⦁ Enlargement of the abdomen
⦁ Rectal pressure
⦁ A lot of urination
⦁ Anemia due to heavy periods
Symptoms of Cysts
⦁ Sharp and dull abdomen pain on one side
⦁ Extremely painful periods
⦁ Tenderness of the breasts
⦁ Bowel problems
⦁ Heavy uterine bleeding
⦁ Gaining weight
⦁ Hurting lower back and thighs
⦁ Bloating
If the cyst ruptures, then the following symptoms will be experienced
⦁ Intense abdominal pain that arises suddenly
⦁ Fainting
⦁ Dizziness
⦁ Rapid breathing
⦁ Heavy bleeding
Causes of Cysts and Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are linked to estrogen and progesterone levels. These are the hormones that are responsible for stimulating the development and growth of the uterine lining. The more the level of these hormones, more is the risk of developing fibroids. The exact cause is still unknown but some reasons can be listed as
⦁ Family history of fibroids
⦁ Pregnancy
⦁ Age
⦁ Obesity
⦁ Consuming a lot of red meat
⦁ Alcohol consumption
⦁ Vitamin D deficiency
⦁ Early menstrual cycle
However, the ovarian cyst is greatly related to the menstrual cycle. Some common reasons can be listed as:
⦁ Polycystic ovary syndrome
⦁ Endometriosis
⦁ Pregnancy
⦁ Severe pelvic infection
Treatment Options for Fibroids and Cysts
Fibroids don’t usually need treatment because they will be harmless. Some fibroids are capable of causing infertility by causing inflammation in the uterine lining, the changes in the local hormonal environment cause problems in conceiving.
If the fibroids are too large that they interfere with conception and are leading to severe symptoms, then the treatment options can be
⦁ To reduce heavy bleeding, hormonal contraceptives can be used
⦁ Fibroids can be removed surgically
⦁ Endometrial ablation
⦁ Medication
⦁ Uterine artery embolization
⦁ MRI-focused ultrasound
⦁ Hysterectomy
Treatment options for cysts are mostly required only if the cyst ruptures or is abnormally large, the treatment options can be mentioned as:
⦁ Wait and watch approach
⦁ Pelvic ultrasound
⦁ Cancer tumor marker blood test
⦁ Birth control / oral contraceptives
⦁ Cystectomy
⦁ To lower the risk of cyst development, hormonal contraceptives can be taken
⦁ To remove smaller cysts minimally invasive surgery options can be used
⦁ Oophorectomy can help remove the ovary