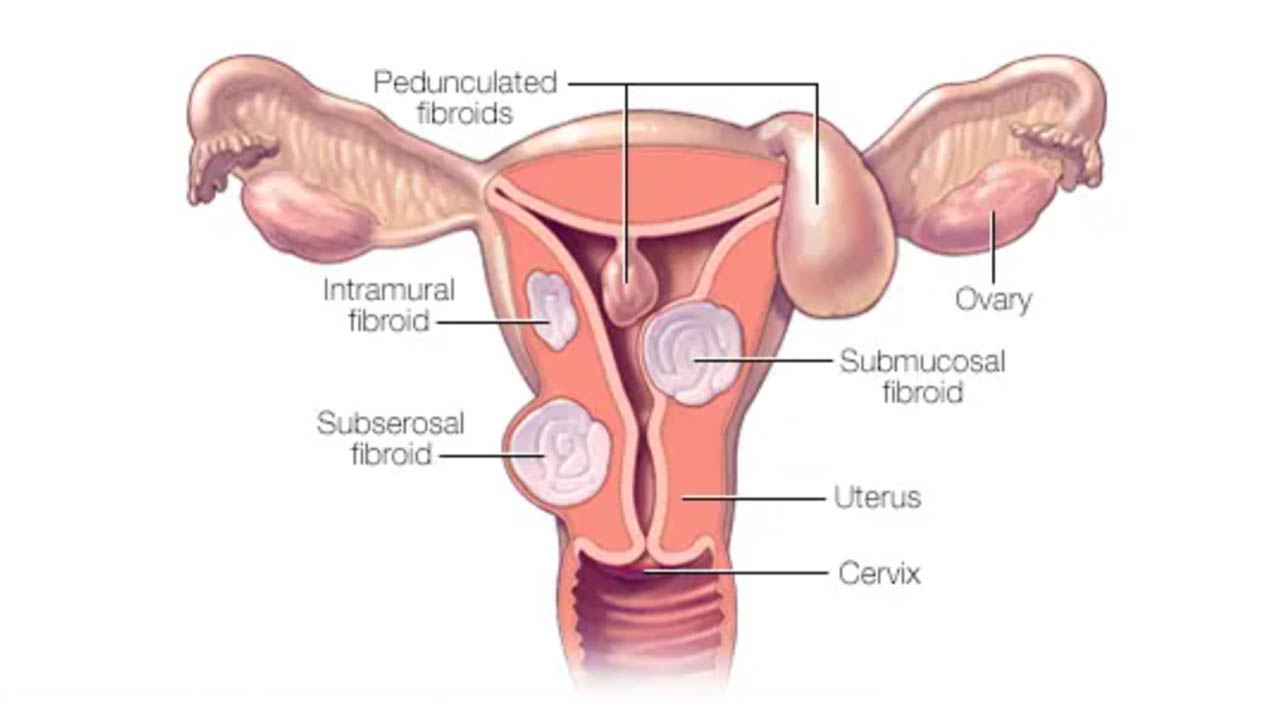
How Can Uterine Fibroids Affect Fertility and Pregnancy? Between 20% and 80% of women of reproductive age are thought to be affected by uterine fibroids, which are benign growths that form in the uterine wall. While most women with fibroids experience no symptoms, some may experience heavy or prolonged menstrual periods, pain during sexual intercourse, and lower abdominal pressure or pain. In some cases, uterine fibroids can significantly impact fertility and pregnancy.
Fertility
Uterine fibroids affect fertility negatively by altering the shape and structure of the uterus, making it difficult for a fertilized egg to implant and grow. The fallopian tubes may occasionally get blocked by fibroids, preventing the egg from entering the uterus. Furthermore, fibroids may alter the cervical mucous, which makes it challenging to conceive. Moreover, fibroids can interfere with ovulation and disrupt the average hormonal balance, leading to infertility.
In some cases, fibroids can cause hormonal imbalances, leading to irregular menstrual cycles and decreased ovulation. Women with fibroids are also more likely to experience infertility than those without fibroids, particularly if they have large or multiple fibroids.
Pregnancy
Uterine fibroids can also have an impact on pregnancy. In some cases, fibroids can cause miscarriage, premature labor, or placental abruption, a condition in which the placenta separates from the uterus before delivery. Fibroids can also make it difficult for a fetus to get into the optimal position for delivery and cause complications during delivery, such as obstructed labor.
In some cases, fibroids can also lead to premature delivery, increase the risk of postpartum hemorrhage, and cause difficulty with breastfeeding. Cesarean delivery is when the baby is delivered through a uterine incision. This condition is highly likely if the patient has suffered from fibroids recently.
Diagnosis
It is crucial to visit a healthcare specialist if you are struggling with infertility or are worried about how uterine fibroids may affect your pregnancy. Your provider will conduct a physical examination, including a pelvic exam, and may perform an ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to assess the size and location of any fibroids.
Treatment
Surgical removal of uterine fibroids The size and location of the uterine fibroids, the symptoms, and future pregnancy goals all influence how the condition is treated. Vascular Specialists recommend myomectomy or hysterectomy for women who are not planning to become pregnant. For women planning to become pregnant, non-surgical options, such as medication or hormonal therapy, may be recommended.
Another purpose of hormonal therapy is to control menstrual cycles and lessen severe bleeding from uterine fibroids. In some cases, women may choose to delay treatment until after pregnancy. Regular monitoring and close observation of symptoms are essential in these cases to ensure the fibroids do not cause complications during pregnancy.
Conclusion
Uterine fibroids can significantly impact fertility and pregnancy, but with proper diagnosis and treatment, women can manage their symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. See a doctor if you’re dealing with infertility or have questions about how uterine fibroids may affect your pregnancy.