Uterine fibroids and uterine polyps are abnormal growths that appear within the uterus. However, they differentiate in symptoms, causes, and treatment options. Understanding the difference between both conditions is crucial for seeking proper medical attention. In this article “Uterine Fibroid Vs Uterine Polyps” we will discuss the key differences between the two terms and their symptoms.
Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are benign growths within the uterus from its muscle tissue. They are non-cancerous and are also known as myomas or leiomyomas. They vary in size, shape, and location. Fibroids are mainly categorized into four types based on their location.
- Intramural Fibroids: It is a common type of uterine fibroid that develops within the muscular wall of the uterus.
- Subserosal Fibroids: Subserosal fibroids are a type of uterine fibroid that develops on the outer wall of the uterus, just beneath the serosa, the outermost layer of the uterus. Unlike other types of fibroids, such as intramural or submucosal fibroids, subserosal fibroids grow outward from the uterus, often advancing into the pelvic cavity.
- Submucosal Fibroids: Submucosal fibroids are a type of uterine fibroid arising from the uterus’s muscle tissue. Unlike other types of fibroids, submucosal fibroids grow just beneath the endometrium, the lining of the uterine cavity.
- Pedunculated Fibroids: These fibroids are stalk-like and attached to the uterine wall. They can be found inside or outside the uterus.
Symptoms
Most of the time, uterine fibroids are asymptomatic, but in some cases, they cause a range of uncomfortable symptoms such as:
- Heavy and irregular menstrual bleeding
- Painful menstruation
- Back pain
- Bloating or abdominal swelling
- Fatigue
- Constipation
- Frequent urination
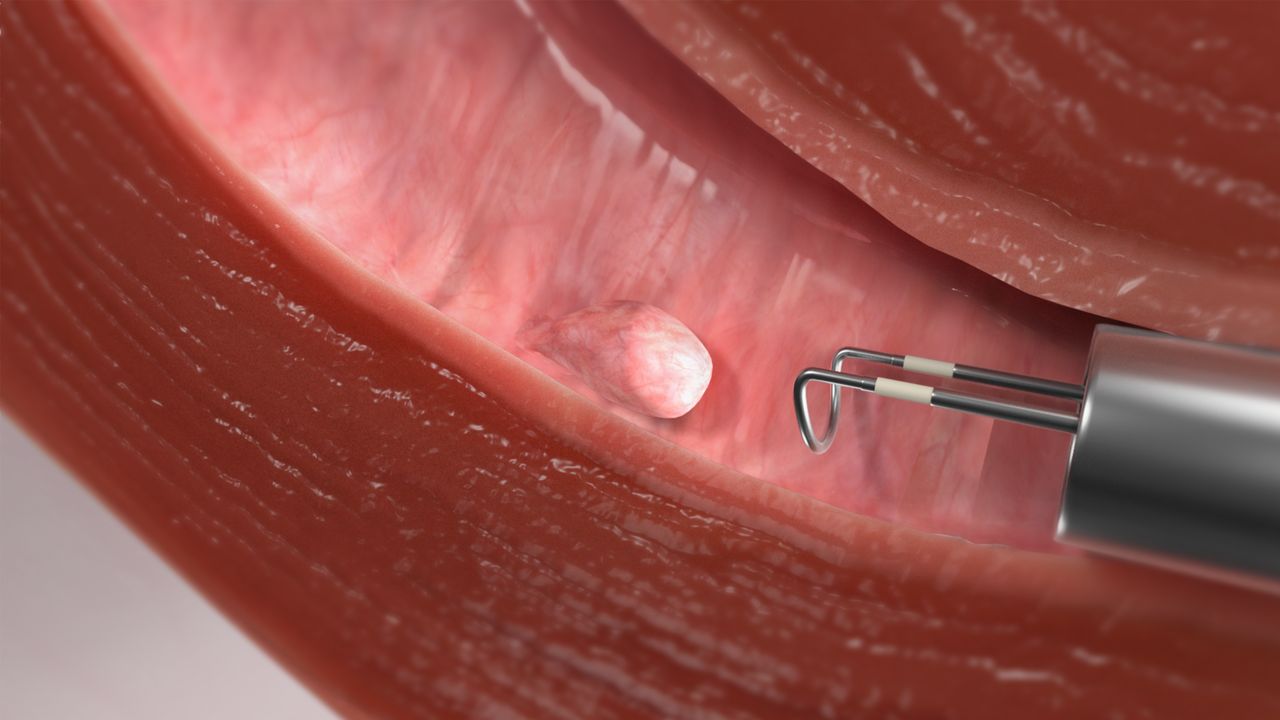
Uterine Polyps
Uterine polyps are abnormal uterine growths, known as the endometrium, from the uterus lining. They are also called endometrial polyps as they contain the same tissue as the uterus lining, unlike uterine fibroids. Polyps can range in size and may be either sessile (flat-based) or pedunculated (attached by a stalk).
Symptoms
- Irregular menstrual bleeding (e.g., spotting between periods)
- Heavy menstruation
- Bleeding after menopause
- Infertility or difficulty in conceiving
Uterine Fibroid Vs Uterine Polyps
Fibroids and polyps share some similarities, but they are distinctive in some features, such as:
- Malignancy risk: Both fibroids and polyps are benign, but polyps may have the potential to turn into cancerous growths, especially in post-menopausal women.
- Composition: Fibroids are composed of the uterus’s muscle tissues. However, uterine polyps comprise the endometrial tissues.
- Size and structure: Fibroids can grow larger and impact the uterus’s overall morphology, whereas polyps are localized within the uterus lining.
Understanding these fundamental differences plays a crucial role in treating the conditions. Although they may require standard diagnostic techniques and treatment options, it is essential to understand the symptoms and consult a healthcare professional for tailored medical advice.