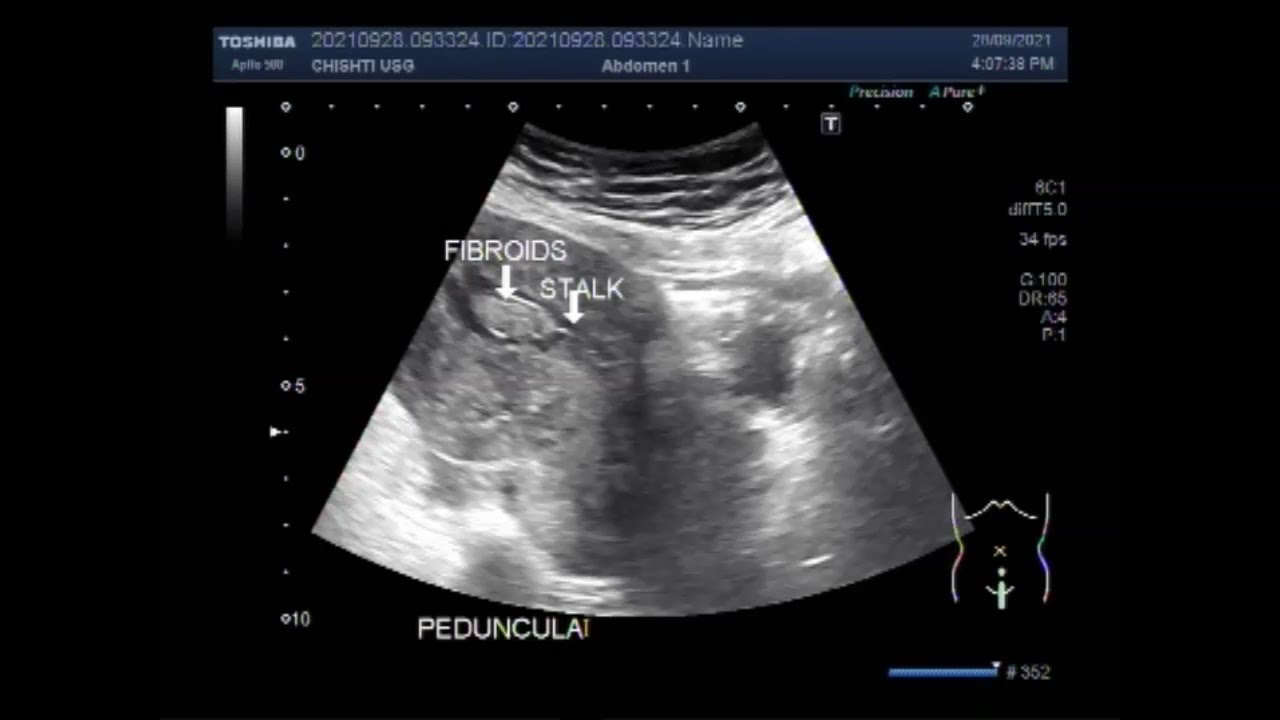
A non-common type of benign tumour that develops within or around the uterus is called pedunculated fibroids. The major characteristic differentiating these fibroids from other types of fibroids is their stalk-like structure that helps in their attachment to the uterine wall. Pedunclutaed refers to the fibroid’s attachment with a stem-like structure (peduncle).
Types of pedunculated fibroids
There are two types of pedunculated fibroids based on their site of attachment.
Pedunculated submucosal fibroids: These fibroids usually grow on the outer side of the uterus and are attached by the peduncle to the wall of the uterus. However, sometimes they may protrude into the pelvic cavity and result in pressing other organs.
Pedunculated subserosal fibroids: These fibroids grow within the uterine cavity and the peduncle is attached to the uterine lining. They are more likely to cause symptoms associated with fertility and menstruation.
Causes and risk factors
Pedunculated fibroids are known to be idiopathic as their exact cause is not fully understood, but some risk factors can contribute to their development, such as:
- Hormones: Hormones such as estrogen and progesterone that regulate the menstrual cycle also promote the fibroid’s growth. These hormones stimulate the growth of fibroids if a woman is in her reproductive years.
- Genetic predisposition: A family history of fibroids increases the likelihood of developing fibroids.
- Age and ethnicity: Women, most commonly between the ages of 30 to 50 years, as well as women of some ethnicities such as African – Americans, are more prone to developing fibroids.
- Lifestyle factors: A sedentary lifestyle, high cholesterol levels, and obesity have proven to be associated with an increased risk of fibroids.
Symptoms
Symptoms of pedunculated fibroids vary depending on their site of attachment within the uterus.
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Pelvic pain and pressure
- Frequent urination
- Constipation
- Infertility and Complications During Pregnancy
- Pain during sexual intercourse
Diagnosis
Pedunculated fibroids are commonly diagnosed during a pelvic examination or through different imaging techniques such as an ultrasound, MRI, or hysterosonography. These diagnostic tests can determine the size and location of the pedunculated fibroids within the uterus.
Treatment options
The treatment options for pedunculated fibroids depend upon the severity of symptoms, age, physical health as well as the site and size. The most common treatment options available for management are:
Medications such as birth control pills, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, and non-hormonal medications can help manage symptoms like heavy menstruation and pain. UFE is being considered as the best minimally invasive treatment option to manage fibroids and their related symptoms.
Surgery
Surgical options such as myomectomy (a surgical procedure to remove the fibroids while preventing the uterus) or hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) are the options available to treat fibroids considering the severity of symptoms and other major life choices of the patient.
Pedunculated fibroids are a common gynecological condition that can potentially impact a woman’s quality of life. Most of the time, these types of fibroids are non-cancerous and often asymptomatic. However, they can cause a range of uncomfortable symptoms that may require proper medical assistance. An understanding of the risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for managing the condition and improving overall well-being.