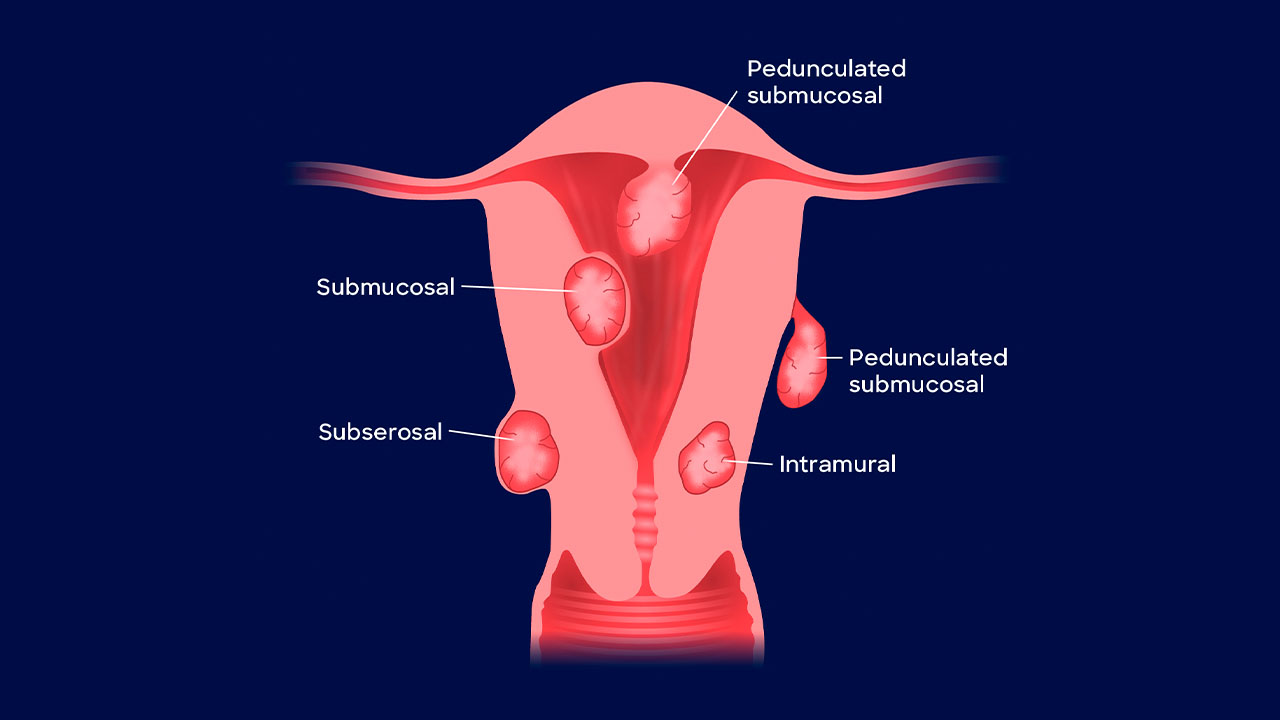
Uterine fibroids have many types, and submucosal fibroids are one of them. They are benign tumors that arise from the uterus’s muscle tissue. Unlike other types of fibroids, submucosal fibroids grow just beneath the endometrium, the lining of the uterine cavity. Due to their location, these fibroids can have a substantial impact on menstrual bleeding and fertility, making them a particular problem for women of childbearing age.
Causes and Risk Factors of Submucosal Fibroids
Submucosal fibroids are known to be idiopathic as their specific cause is not fully understood, but some factors can contribute to their development, such as:
Hormonal Influence
Estrogen and progesterone hormones regulate menstrual cycles. Moreover, they can also promote the growth of fibroids. These hormones activate during a woman’s reproductive years, promoting fibroid growth. After menopause, fibroids often decrease in size due to a descent in hormone levels.
Genetic predisposition
Fibroid development is more likely in families where fibroids have already occurred. Women are more likely to acquire fibroids if their mother or sister has a history of the condition.
Age and ethnicity
Women, most commonly between the ages of 30 to 50 years, are more prone to developing fibroids. According to research, American and African women are more likely to develop fibroids at a younger age than women of other ethnicity.
Lifestyle
Factors such as a sedentary lifestyle, high cholesterol levels, and obesity are associated with an increased risk of developing fibroids.
Symptoms of Submucosal Fibroids
Submucosal fibroids can cause symptoms related to their impact on the uterine lining. The severity of symptoms commonly depends on the size and location of the fibroid within the uterus. Common symptoms include:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Inter-menstrual bleeding
- Painful menstruation
- Infertility and pregnancy complications
- Pelvic pain and pressure
Diagnosis
Typically, submucosal fibroids are diagnosed through different techniques such as MRI, ultrasound, hysteroscopy, or hysterosonography.
Treatment options
The treatment options for submucosal fibroids depend upon the severity of symptoms, age, physical health, and size of fibroids. The most common treatment options available to manage fibroids are:
Medications
The medication of choice for treating fibroids are birth control pills, gonadotropin agonists, and other non-hormonal drugs.
UFE
Uterine Fibroid Embolization is a widely used minimally invasive procedure for fibroid treatment. It is considered to be an ideal treatment option for women.
Surgery
Surgical options, such as myomectomy or hysterectomy, are available to treat fibroids, considering the severity of symptoms and the patient’s other major life choices.
Submucosal fibroids are a common gynecological condition that can impact a woman’s quality of life. Most of the time, these fibroids are non-cancerous and often asymptomatic, but they can cause a range of uncomfortable symptoms that may require proper medical assistance. Understanding the risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options is vital in managing the condition efficiently.