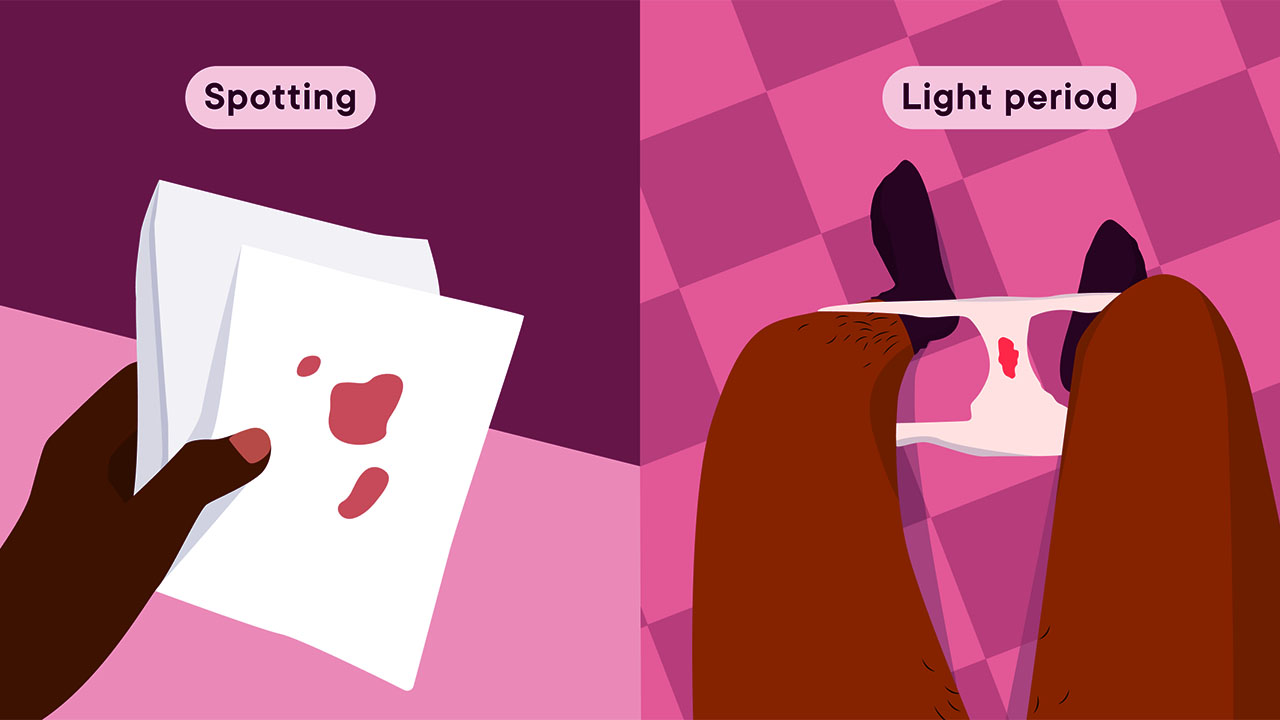
What is spotting? It is the light bleeding outside your menstrual cycle specifically between your periods. Spotting can be minimal as a few drops of blood can not fill a pad or tampon. Depending on the cause, it may last only a few hours to some days. Using a single panty liner can be enough to deal with it.
Difference Between Spotting and a Period
The major difference between a period and spotting is that periods are characterized by heavier blood flows that follow a proper pattern while spotting is much lighter and involves a small amount of blood.
Why does it happen?
Spotting is not a complicated or threatening condition but understanding its causes is essential to evaluate your reproductive well-being. Here are some major causes that led to the phenomenon.
Ovulation
Many women may experience ovulation spotting as a second period. The release of an egg from the ovaries that typically occurs 10 to 14 days after getting your period is termed ovulation. Spotting during the ovulation phase can also be experienced as a second mini-period. During ovulation uterine lining shreds lightly due to elevated estrogen levels.
Hormonal imbalance
Any imbalance within the hormones can be a leading cause of spotting. Hormones such as estrogen and progesterone are responsible for regulating the normal menstrual cycle. Certain conditions such as weight gain or loss, thyroid disorders, and PCOS can disrupt the normal hormonal balance. An imbalance within the hormones causes the uterine lining to shed lightly.
Birth control
Starting or changing your birth control has an elevated effect on your menstrual cycle. Birth control such as hormonal pills, patches, or IUDs disrupt normal hormonal balance leading towards spottings between your periods.
Implantation bleeding
One of the earliest indications of pregnancy can be implantation bleeding. When a fertilized egg attaches to the lining of the uterus light spotting occurs. It generally takes place during 6 to 12 days after conception. Embryo embedding in the uterine wall can cause this phenomenon.
Perimenopause
Perimenopause is the transitional phase before menopause. Women who are in their 40s and early 50s might experience perimenopause which can impact the frequency of periods as well. During this phase hormones highly fluctuate to prepare the body for menopause due to which the uterine lining sheds unpredictably resulting in spotting.
Infections
Vaginal infections, sexually transmitted diseases, and complicated UTIs irritate the cervix and uterine lining leading to spots.
Uterine fibroids or polyps
Uterine fibroids or polyps disrupt the normal uterine lining and put pressure on the blood vessels resulting in spotting or intermittent bleeding between periods. Spotting is a common and harmless phenomenon experienced by various women. Several factors can be a potential cause. Understanding the pattern and accompanying symptoms can help diagnose some conditions at their earliest stages.