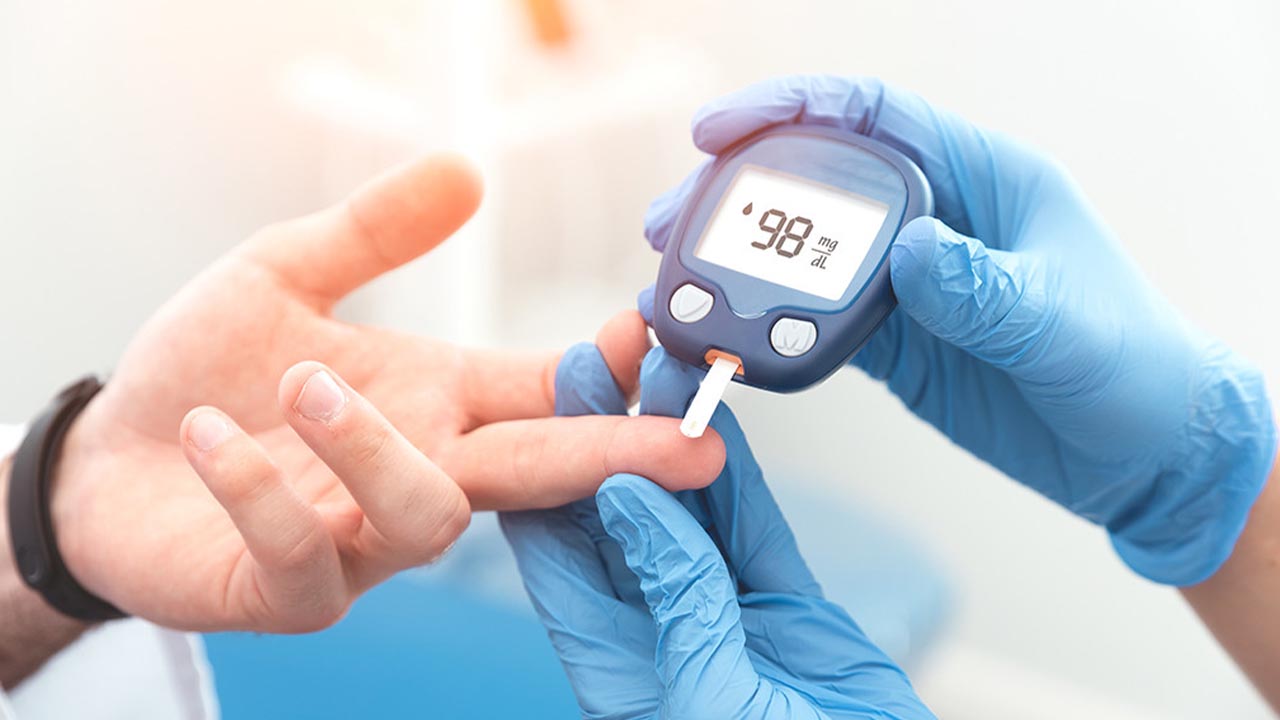
Older age welcomes minor and major health issues if physical and body health is ignored. One such severity is diabetes which is common in older individuals comprising 33% of the elderly. The intensity of diabetes may vary from mild to extreme, concerning the age factor and lifestyle modifications. It takes a lot of effort, medication, doctor recommendations, nutritionist guidance, and exercise to maintain blood glucose levels to optimum, which helps older people to survive while suffering from Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. Management of diabetes in old age is tough but not impossible.
Therapeutic options for diabetic prevention in the older population
Apart from the conventional pharmacological intervention in the treatment of elderly diabetes, there are therapies available which can be a possible aid in controlling diabetes. Educating elders about proper diet and adequate exercise is the first step in promoting awareness of natural diabetic cures. Based on the patient’s needs and preferences, glucose-lowering therapies, which involve oral anti-hyperglycemic agents, are to be implemented.
Management of elderly diabetes by medication
Diabetic management in older people is an individualized approach that relies on how the patient’s body reacts to the medicinal treatment. Different types of medicines are explored for their potential treatment efficacy in older people with diabetes. Some of the notable medicines are
- Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors
- Glucophage
- Glucotrol
- Thiazolidinedione
- Sulfonylureas
- Metformin
- Glyburide
- Glimepiride
- Insulin
The importance of management of diabetes in old age is emphasized as diabetes in the elderly welcomes other health issues too. One such identified issue is long-term vascular complications that can lead to poor blood circulation and weakened bodily strength due to high blood glucose levels. Renal failure and hepatic dis-functioning are two other complexities that can result from prolonged elderly diabetes, so the main focus is to control hypoglycemia.
Prevention of diabetes in old age
Some older individuals are weak to the stage that they cannot recover their poor diabetic health preliminary by eating a good diet and exercising. These are recommended to consume
- Insulin hormonal injection
- Medication pills
- Consume healthy drinks and keep yourself hydrated with water
- Avoid higher sugary content meals
- Control blood pressure to avoid hypertension state
- Lipid controls
- Aspirin therapy
Diabetes encountered in older age cannot be treated completely or vanish from the body, but it requires a tailored care plan for the patients to keep up with their sugar levels. With progressive age, insulin resistance and glucose tolerance reduce significantly, which are the prime reasons that make diabetes harder to control. However, indirect therapeutic options are still applicable to try on older adults.
Lifestyle modifications: a common elderly diabetic management approach
Nutritional evaluation of older adults suffering from different types and severities of diabetes is necessary to advise them about some precautions. Obesity and fasting blood glucose levels are two parameters that are observed and targeted in elderly patients. Doctors suggest that caloric restriction and loss of 5% of weight body are beneficial for the health of elderly diabetics with obese bodies. In addition, minimal or no alcohol, caffeine, tobacco, and harsh chemicals are good for health deteriorating from diabetes.