Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in the United States. Angioplasty is a medical procedure used to improve blood flow through vessels that have been narrowed or blocked.
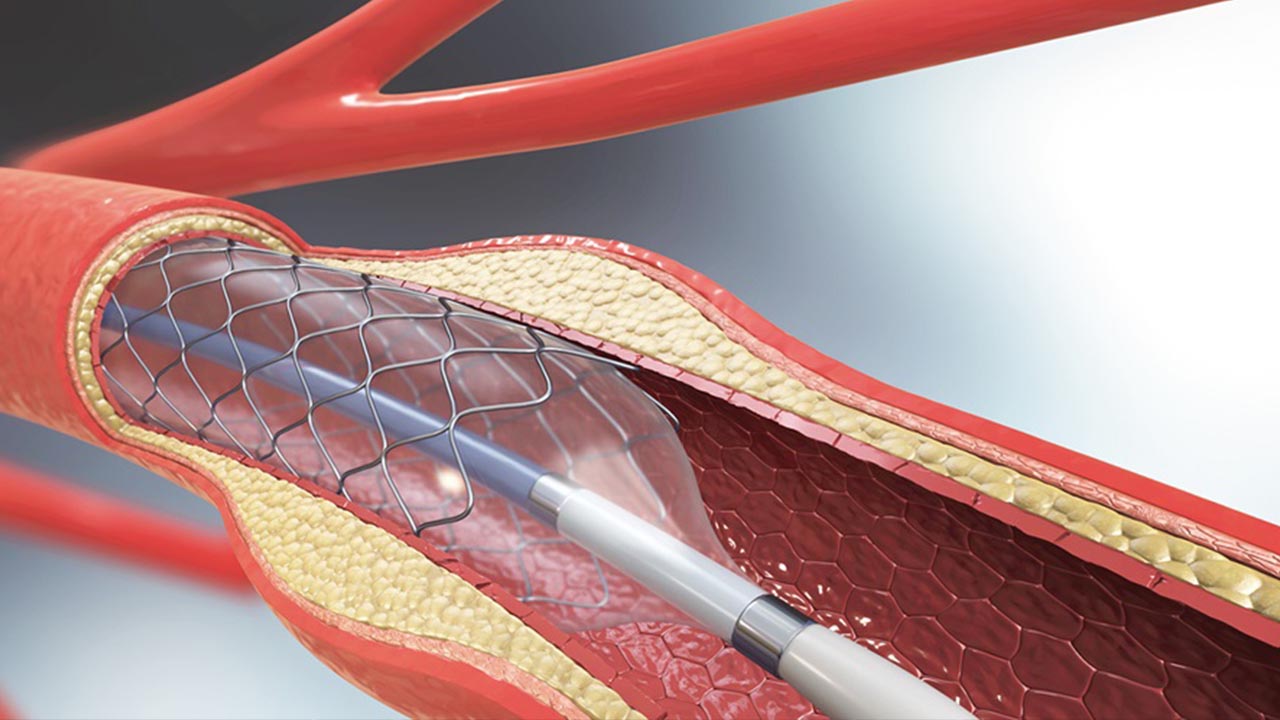
Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in the United States, so it’s important to be aware of procedures that can improve blood flow and alleviate symptoms. Angioplasty is a medical procedure used to improve blood flow through vessels that have been narrowed or blocked. This minimally invasive procedure involves inserting a small balloon into the vessel and inflating it to widen the area. In some cases, a stent may also be placed in order to keep the vessel open. Angioplasty can often be done on an outpatient basis and has minimal recovery time.
What is the procedure for angioplasty?
A physician inserts a sheath into a patient’s artery during angioplasty through a catheter inserted in the groin or arm. The catheter is then advanced to the area of the obstructed vessel. A contrast dye is injected through the sheath and into the vessel to aid in locating the blocked area of the vessel.
A deflated balloon is then advanced through the catheter, over a guide wire, to the blocked area. The balloon is inflated once it is in place to flatten and expand the area where the blockage is located. The balloon is then deflated and removed. The balloon is then exchanged for a flexible metal stent that is placed in the area where the blockage occurred. The stent is expanded to open the unobstructed vessel.
What is the purpose of the catheter?
The catheter is a long, soft, hollow tube made of latex, platinum, or stainless steel, which is inserted into the artery.
What are the risks of angioplasty?
There are a few risks to angioplasty, but they are not uncommon. Some of the risks include bleeding, blockage coming right back, and stroke. But those risks are very, very small.
As a general rule, the more times your artery is touched, the more risks there are. But most people do not have to worry about this happening to them. While it may sound scary if someone is telling you about the risks, it really should not be. These risks can be easily managed.
For instance, if you have a stent put in, you need to take a blood thinner.
The risk of death from angioplasty is only about 1 in 1,000. There are some risks to not getting angioplasty. They are not immediate, but there are still risks. They include very slow healing wounds and problems that would later lead to amputation of the limb.
In fact, a blockage that comes right back after angioplasty is the same thing as when a person gets a stent and it doesn’t work, so the chance of POSSIBLE complications with angioplasty is about the same as getting a stent and it doesn’t work for you.
First, we talked about blockage, and blockage can come back in a few ways. Blockage can come back from where you have a blockage.
In fact, those risks are the same as the risks of doing nothing. There are no long-term risks that have been shown to be associated with angioplasty. The risks are important to consider, but it is important to know that the risks are small. Your doctor will go over these with you.
There is always a risk of dying during surgery, and this is mainly dependent upon your health and your age. Each center has different statistics, and you should know the numbers for your center. Your doctor should go over these with you prior to catheterization.
The risks are very small, and the treatment will be a life-changer. You should consider it as soon as you can.
What are the costs of angioplasty?
Cardiologists charge several thousand dollars for performing the procedure.