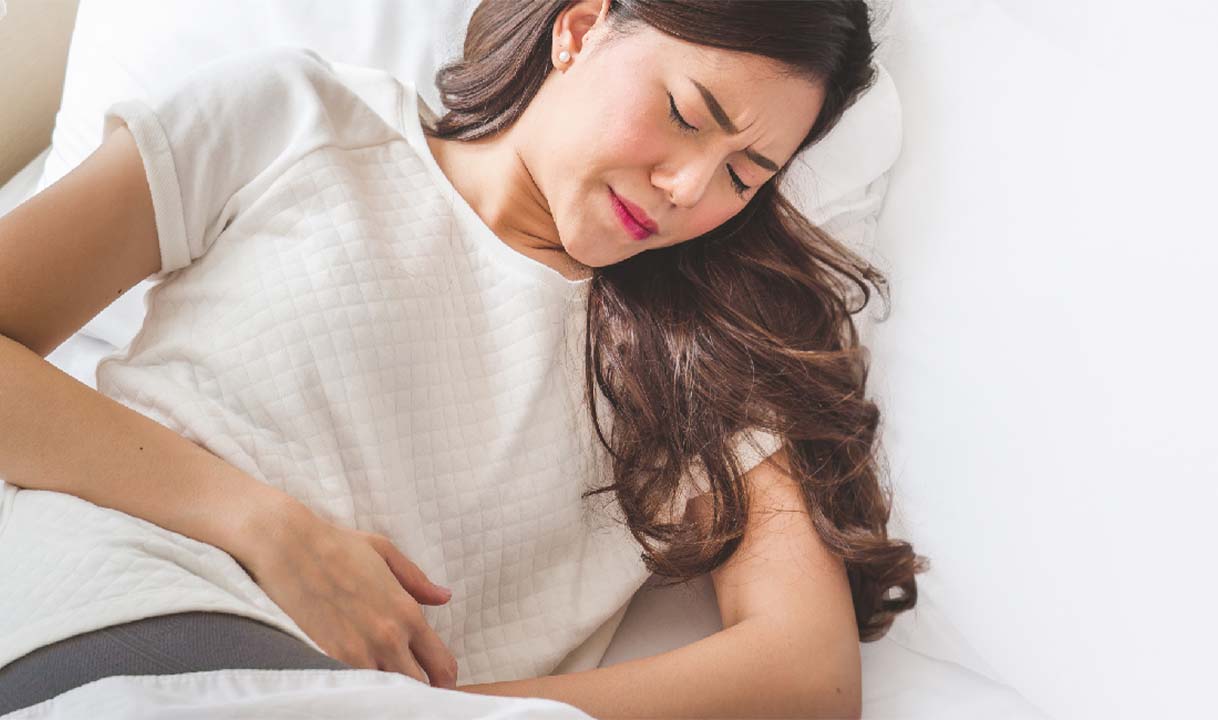
The condition when uterine fibroids pass out of a woman’s body is called fibroid expulsion. Even though the sound seems scary, this health condition is rare and causes almost no symptoms. However, cases where fibroid expulsion are usually associated with Uterine fibroid embolization (UFE). UFE is a non-surgical, minimally invasive treatment to shrink fibroids’ size and minimize their symptoms. Women who undergo the procedure of UFE are usually concerned about what is fibroid expulsion.
Fibroids:
The non-cancerous growths of the uterus are known as uterine fibroids. These can be identified in a normal routine pelvic exam or diagnosed by ultrasound and lab tests. This condition can cause irregularities in a woman’s uterus’s size and shape. These are the root cause of fibroid expulsions if you get it treated via uterine fibroid embolization.
Causes:
The procedure, UFE, restricts the blood supply toward uterine fibroids. This leads to the shrinkage of the fibroid to minimize the symptoms associated with fibroid. In a few circumstances, these fibroids, left starving for blood, pass out of one’s body through the vagina. The fibroid may pass completely, partially, or in pieces. The fibroid expulsions may fall out with the menstrual blood.
Symptoms:
Researchers have found that only 4.9% of the women who undergo UFE have experienced fibroid expulsion after about 3-4 months of the procedure. Of this percentage, only 5% show symptoms related to the expulsion, i.e., vaginal discharge and cramping. The women who experience the expulsion symptoms are a sign that they undergo a bulk expulsion. Almost 89% of the women who experience symptoms have a bulk expulsion.
The vaginal discharge develops as a result of expulsion following the UFE treatment. A discharge with an unpleasant odor can indicate infection; you should contact your doctor immediately.
Medical Interventions:
Fibroid expulsion can easily occur without any medical interventions. Almost half of the cases occur at home or with a minimally invasive transvaginal process at a doctor’s office. Women who have children are at a greater risk of fibroid expulsion than the ones that do not have children.
However, the fibroids that have partially passed out would require further medical interventions. The need to remove the fibroid expulsion via gynecological treatment still stays. Other women may require hysteroscopic fibroid resection, in which the fibroid with removed using a scope as a guide.
Hysterectomy:
Fibroid expulsion can potentially risk a woman if only the fibroid has not been passed out completely, either naturally or surgically. In such cases, the risk of infections increases and will require a hysterectomy. However, a low percentage of women would require an urgent hysterectomy.
What should be done?
If you think you are experiencing the symptoms of fibroid expulsion, you should immediately consult your radiologist, who performed UFE for your fibroid. You can work with your doctor and devise an action plan.
Communication:
To successfully manage your health condition, you should be able to communicate it properly. Proper collaboration between the doctor and patient is the key to eliminating any symptoms and associated risks.
In conclusion, this article highlights the complications associated with uterine fibroid embolization treatment, fibroid expulsion. The complications usually occur 3 months after the procedure. That is why fibroid expulsion is one medical condition that makes the follow-up checkup important 6 months after the Uterine Fibroid Embolization treatment.